Speakers: Jose Barreto, Steven Ekren
Pre-session question … How far can a cluster stretch? You can have your heartbeat up to 1 minute timeout. They recommend no more than 10-20 seconds. However there is a license mobility limit – it is pretty long distance, but it does exist.
Moving Physical to the Private Cloud (Virtual)
Many ways to P2V from rebuilt, disk2vhd, backup/restore, VMM, and on and on and on.
VMs can be HA on Hyper-V. Cost reductions and mobility by virtualization. Easier backup. Easier deployment. Easier monitoring. Flexibility. Self-service. Measurability. Per-VM/VHD VM replication is built in with Hyper-V Replica. And on and on and on.
VM Monitoring added in WS2012 Failover Clustering
2 levels of escalated action in response to a failure trigger:
- Guest level HA recovery
- Host level HA recovery
Off by default and requires configuration. Watch for an alert, say from a service. If service fails, cluster gets the alert and restarts the service. If within an hour, the cluster gets the same alert again, it’ll fail it over (shut down) to another host.
Requires that the VM is WS2008 R2 or later and in the same domain as the hosting Hyper-V cluster.
In the private cloud:
- Guest OS admin configures the failure triggers
- Recovery from host is configured by the cloud admin
The process works through the Hyper-V heartbeat integration component in the guest OS. An “application critical flag” goes back to the parent partition via VMMS, and escalated in the host via the VM resource in the cluster, to the Cluster Service.
You can enable VM Monitoring in WS2012 in the VM properties (cluster) in Settings. The cluster will still get a signal, if configured in the guest OS, but it is ignored. Basically cloud admin can disable the feature, and it ignores what the tenant does in their VM.
Event ID 1250 will be registered in System log with FailoverClustering source when the application critical flag is sent.
We can set up a trigger for a service failure or an event.
Add-ClusterVMMonitoredItem … Get-, Remove-, Reset- are run by a guest OS admin in the VM.
You can also hit Configure Monitoring action on a VM in Failover Cluster Manager on the cloud. Assumes you have admin rights in the VM.
Guest Clustering
We can create guest OS clusters. Protects against faults in the guest layer, e.g. BSOD, registry issue, etc. Also allows preventative maintenance with high SLAs.
Can use: iSCSI, virtual fiber channel, or SMB 3.0 shared storage.
Guest Clustering and VM Monitoring
You can use both together.
Set cluster service restart action to none for 2nd and 3rd failure in the guest cluster node OS. First failure is left at Restart the Service.
Then from the host site, enable VM monitoring for the guests’ Cluster Service.
Demo of virtual SOFS
Steven kills the cluster service on a SOFS node using Process Explorer. The service restarts. Video being streamed from the SOFS via that node pauses and resumes maybe 2-3 seconds later. He kills the service a second time. The host cluster shuts down the VM and fails it over.
Thorough Resource Health Check Interval defaults to 1 minute in the VM properties in Failover Cluster Manager. You can reduce this if you need to, maybe 20 seconds. Don’t make it too often, because the check does run a piece of code and that would be very inefficient.
Jose comes on stage.
Shared Virtual Disks
Before WS2012 R2, the only way we could do guest clustering was by surfacing physical/cloud storage to the tenant layer, or by deploying virtual file servers/iSCSI. First is insecure and inflexible, second is messy. Hosting companies just won’t want to do it – and most will refuse.
With WS2012 R2, VMs can share a VHDX file as their shared data disk(s). It is a shared SAS device from the VM’s perspective. It is for data disks only.
There are 2 scenarios supported:
- Using CSV to store the VHDX
- Using SMB to store the VHDX
The storage location of the CSV must be available to all hosts that guest cluster nodes will be running on.
This solution isolates the guests/tenants from your hosts/cloud fabric.
Deploying Shared VHDX
Use:
- Hyper-V Manager
- PowerSHell
- VMM 2012 R2
Think about:
- Anti-affinity, availability sets in VMM service templates. Keep the guests on different hosts so you don’t have a single point of failure.
- Watch out for heartbeats being too low.
Deploy the data disk on the SCSI controller of the VMs. Enable sharing in the Advanced features of the VHDX in the VM settings.
In the VM, you just see a shared SAS disk. You can use an older version of Windows … 2012 and 2012 R2 will be supported. This is limited by time to test older versions.
PowerShell:
- New-VHD
- Add-VMHardDiskDrive …. –ShareVirtualDisk < repeat this on all the guest cluster VMs
- Get-VMHardDiskDrive … | ft VMName, Path, ControllerType, SupportPersistentReservations < the latter setting indicates that it is shared if set to True.
In VMM service template tier properties, you can check Share The Disk Across The Service Tier in the VHDX properties.
Inside the VM, it just looks like a typical disk in Disk Management, just like in physical cluster.
Tip: use different VHDX files for your different data volumes in the guest OS cluster. It gives you more control and flexibility. Stop being lazy and do this!
The hosts must be 2012. The guests are 2012 and 2012 R2, with the latest integration components.
This is only VHDX – it uses the metadata feature of the disk to store persistent reservation information. Can use fixed or dynamic, but not differencing.
Backup
Guest-based backup only. Host based-backups and snapshots of the shared VHDX are not supported. Same restrictions as with guest clusters using physical storage.
Storage Migration of Shared VHDX
This is not supported – it is being referenced by multiple VMs. You can Live Storage Migrate the other VM files, but just not the shared data VHDX of the guest cluster.
You can Live Migrate the VMs.
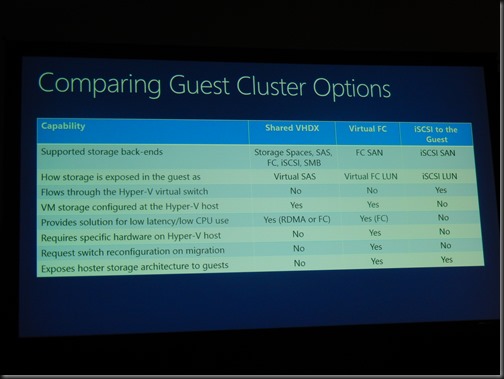
Comparing Guest Cluster Options
Troubleshooting
- Performance counters: Added new counters to PerfMon
- Event Viewer: Hyper-V-Shared-VHDX
- Filter Manager (FLTMC.EXE): The Shared VHDX filter can be looked at – svhdxflt
- Actual binaries of the filer: svhdxflt.sys and pvhdparsersys
Online Resize
You can hot resize a non-shared VHDX in WS2012 R2. You cannot hot resize a shared VHDX.
You can hot-add a shared VHDX.
Unsupported bonus scenario